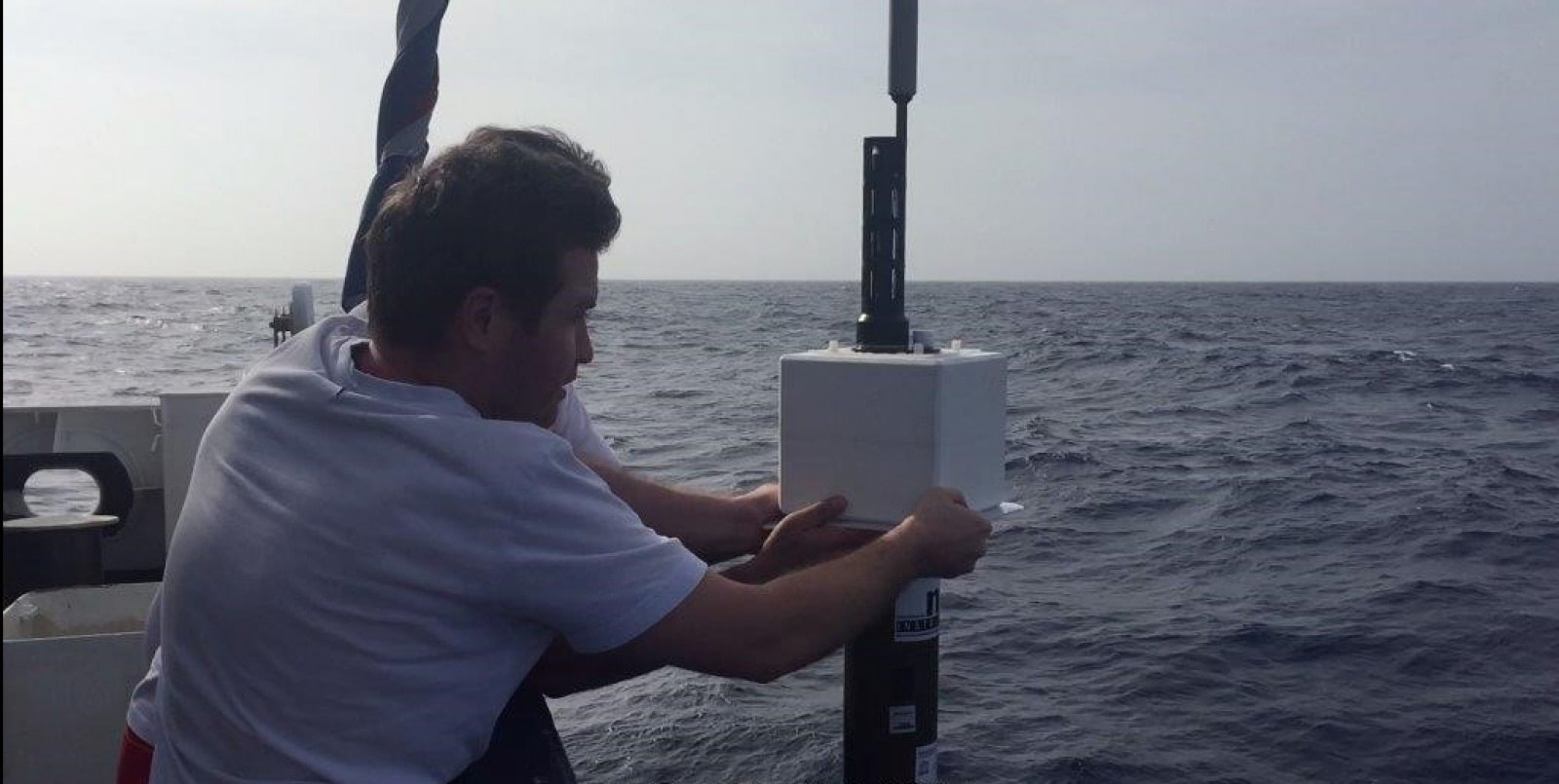
A synergy of science and tourism
Since 2012, KNMI (Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut – Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute) and Oceanwide Expeditions have cooperated in deploying temperature-recording devices, known as Argo floats, at far southern latitudes. Oceanwide’s Antarctica cruises offer a unique opportunity to reach these remote areas. Up to 35 floats have so far been deployed on these voyages, and eight more are on board Oceanwide’s m/v Plancius for this season.

What are Argo floats?
Argo floats, or profilers, are autonomous driving machines that measure water temperature, salinity, and pressure. Though they are meant to be passively transported by the ocean currents, they also actively ascend and descend between the surface and a depth of 2 km (1.2 miles).
A typical operational cycle, shown below, starts with the profiler descending to the parking depth of 1 km (.6 mile), at which position it remains for about 9 days. Afterward it descends to the max depth of 2 km, then immediately rises back to the surface. On the way up, it measures water temperature and salinity.
The data is then transmitted for storage, quality control, and distribution. When transmission is finished, the Argo starts a new cycle by descending to the parking depth again.
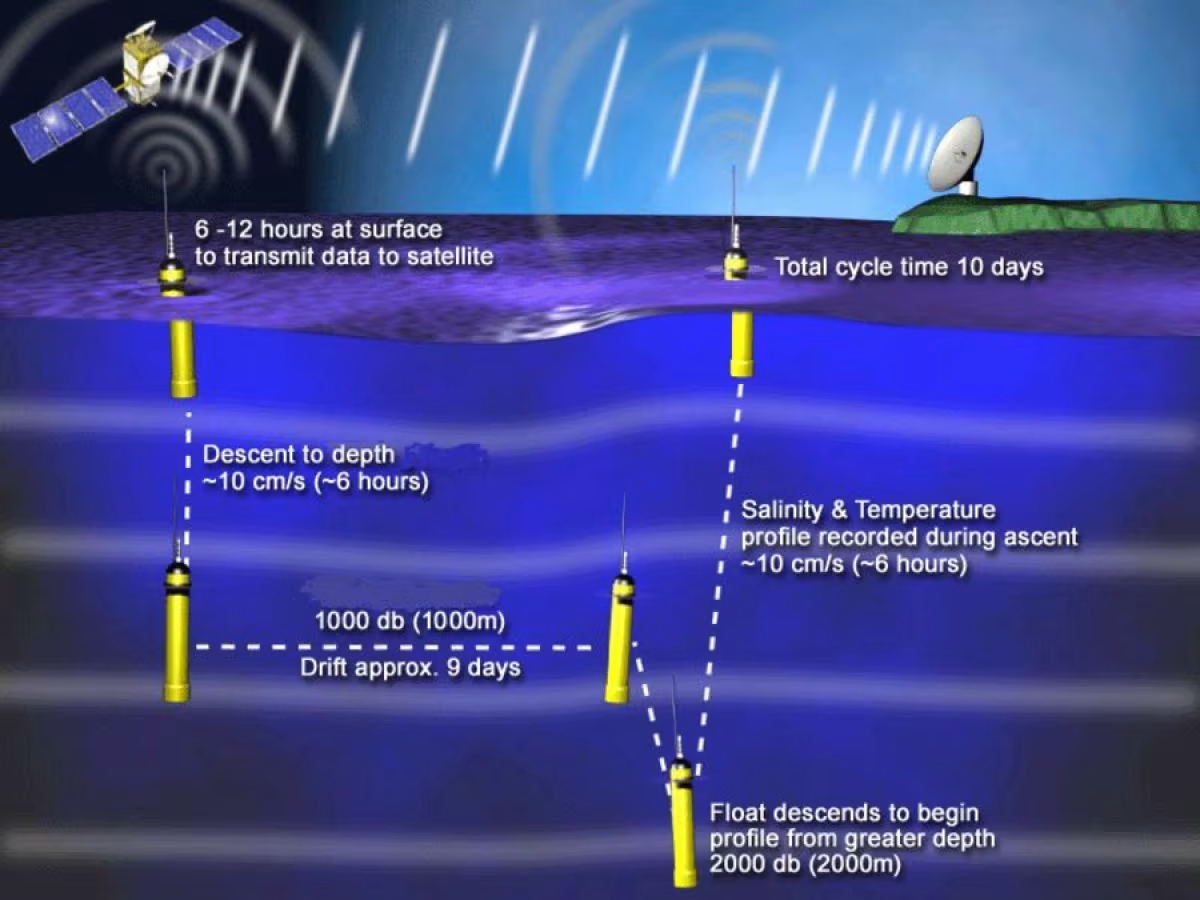
The importance of water temperature and salinity
A vital parameter in oceanography is the density of sea water, determined by temperature and salinity. In general, water density increases with salinity and decreases with temperature. (In other words, warm water is lighter and more saline water heavier.)
The density of sea water in turn determines sea level and pressure. This pressure, and more precisely the pressure differences between points in space, determines oceanic currents. Knowledge of temperature and salinity is therefore essential in understanding currents and sea level.
Since the oceans absorb more than 90% of excess heat trapped in the climate system due to the enhanced greenhouse effect, carefully monitoring ocean temperature is crucial for knowing the processes by which oceans warm.

By Argo Data Management (https://www.seanoe.org/data/00311/42182/) [CC BY 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Argo’s new science of weather forecasting
Seasonal weather forecasts depend on a thorough knowledge of oceanic states. Frequent quality measurements are needed for this. Traditionally these measurements have been made by lowering a probe from a research vessel. These measurements are highly accurate but also time consuming and expensive, so only a few measurements are feasible. Also, they suffer from fair weather bias, as hardly any measurements are made in the Southern Ocean during winter.
Argo floats, on the other hand, are cheap (about €17,000 or $20,000 over a lifetime of four years) and can measure independent of the weather. This means winter measurements in the Southern Ocean are possible for the first time. Once deployed, Argo floats need no maintenance, and data is automatically transmitted to storage centers. This free-flow of information is an essential Argo program principle.

CSIRO [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
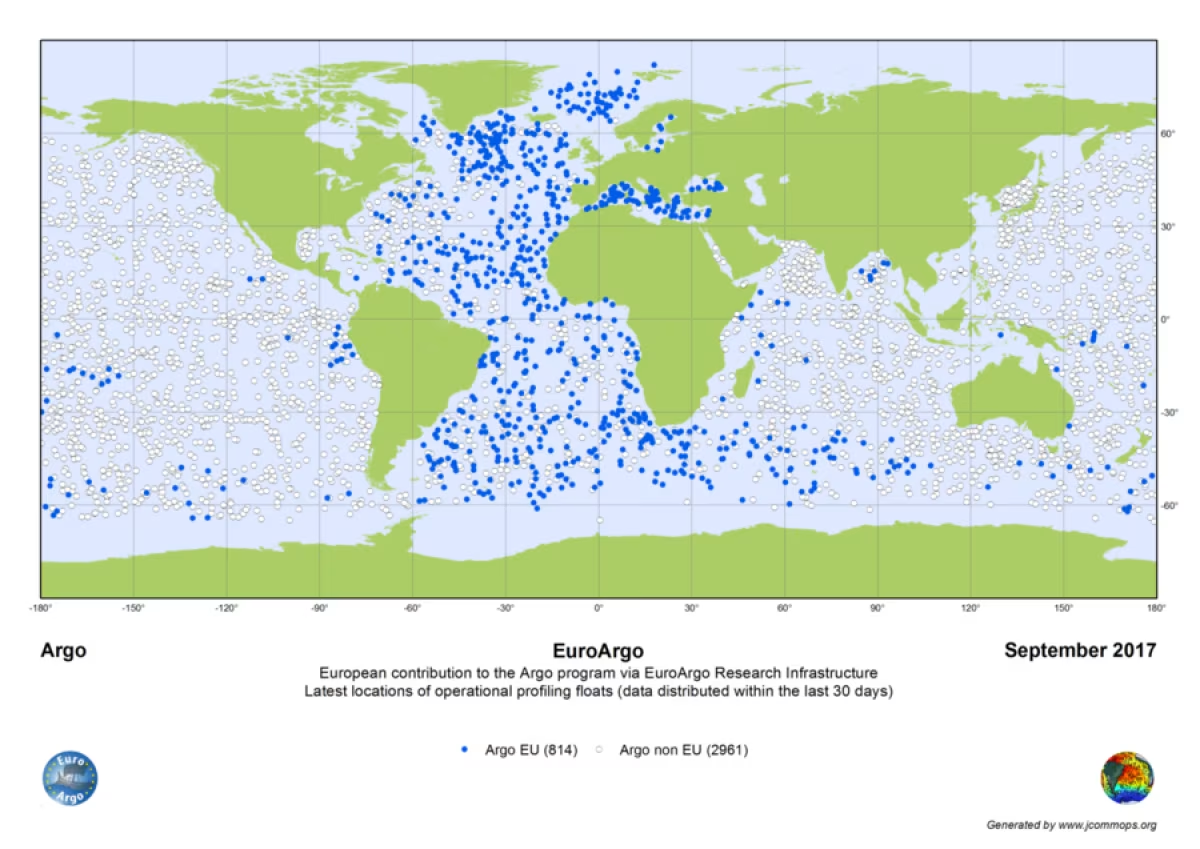
The program behind Argo
Argo is an international research program. Any country or institute can create their own Argo program and contribute data. Institutes from about 30 countries are currently participating. Multiple European countries have even joined to form Euro-Argo and together provide roughly one quarter of all Argo floats. There are nearly 4,000 active floats worldwide.
Argo floats carried on oceanic currents
The image below shows how Argo floats deployed from Plancius in 2014 have been carried by the currents. Because the floats spend most of their time at parking depth (1 km or .6 mile), this picture provides a good illustration of the currents at that depth. The markers along the lines are ten days apart, demonstrating the difference in current depending on the location of the floats.
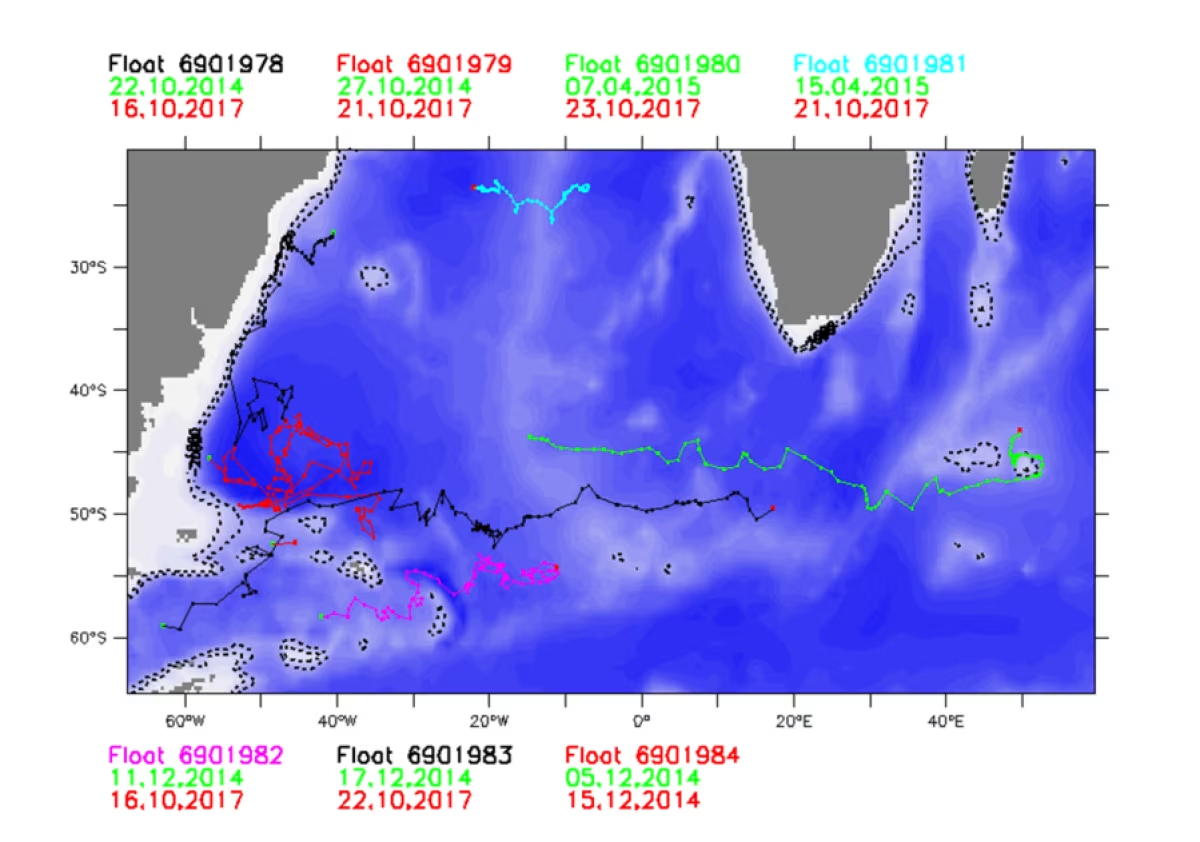
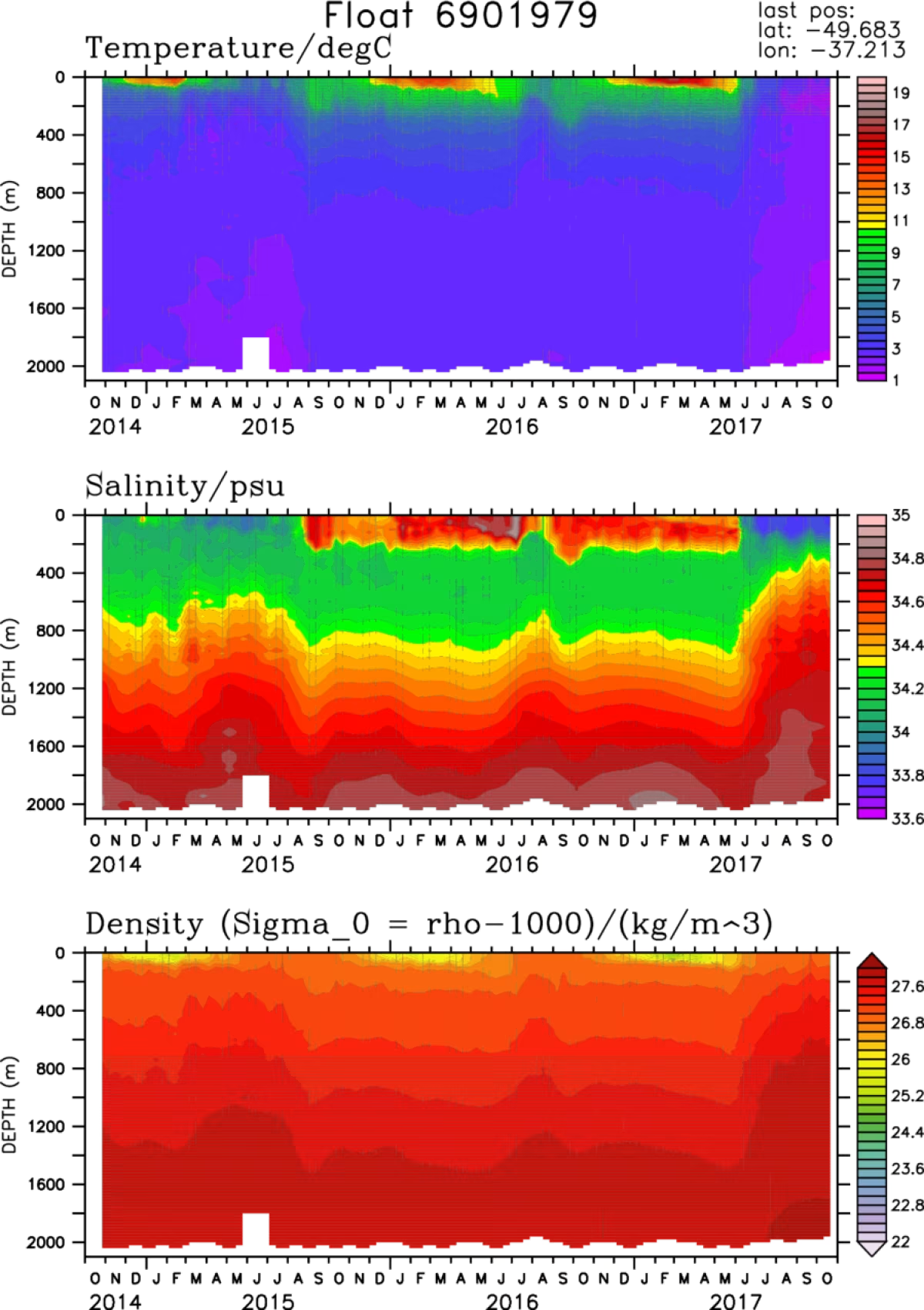
Data from float 6901979
Data obtained from a specific float (the red marker north of South Georgia) shows the loop it made during its first few months of operation. Its surrounding water is fresh and cold, originating in the Drake Passage and flowing north. Only a shallow layer warms in the summer. The picture suddenly changes, however, at the beginning of August 2015: The upper 200 meters (650 feet) become saltier and warmer, showing a clear annual cycle. This water originates from the north. In June 2017, the picture changes again: The Argo float has moved south and again crossed the border between relatively warm water originating in the north, and relatively colder water from the Drake Passage.
For more information, see the following links:
- Argo International for everything about the Argo program
- Argo Information Center for all floats and data
- Euro Argo for the European contribution to Argo and data access







